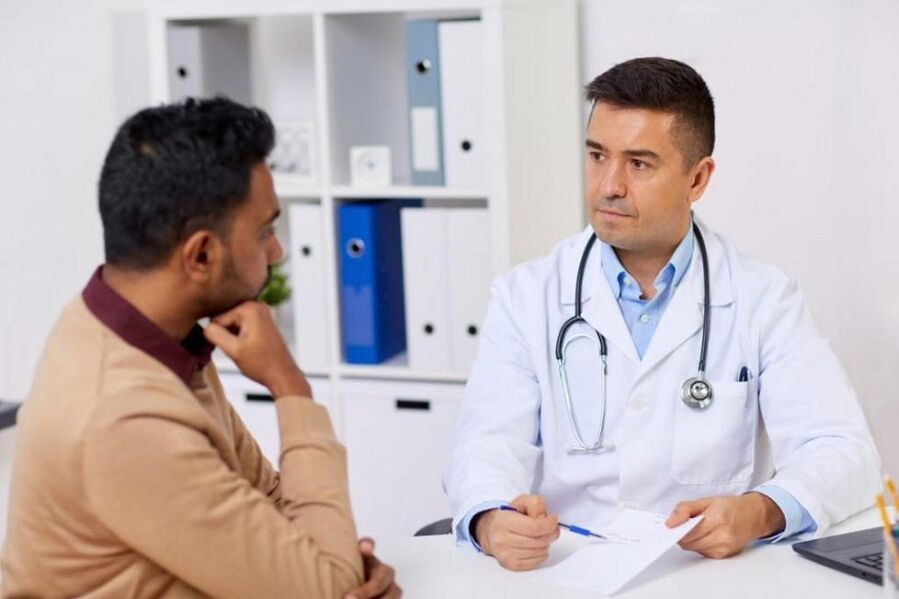
Discharge from the genitals in men appears in the form of a small amount of fluid or mucus, which has a different condition and color. Fluid (mucus) is secreted from the urethra, it is also possible to separate the secretion of the preputial gland, which is located under the skin that covers the head of the penis.
Physiological discharge
- the criteria for urine norm are light golden color, no odors;
- the criteria for the rate of secretion from the prostate are viscous nature, a white tint, a certain sperm odor;
- the criterion for the norm of ejaculate is sperm mixed with the secretion secreted by the prostate, gray in color, having the consistency of mucus;
- the criterion for the smegma norm is a thick white grease.
Smegma (preputial lubricant) accumulates under the foreskin of the penis and is an accumulation of fats and residues of certain bacteria. The lubricant serves to reduce the feeling of friction between the head and foreskin. In different periods of life, the amount of secretion secreted by the preputial glands is different, the peak falls on puberty, and by old age it completely stops.
If hygiene rules are not followed, lubricant (smegma) is collected under the foreskin. Fats are oxidized, and the proteins that make up the composition begin to break down. Simply put, the process of decay sets in. The color of the lubricant becomes greenish, a putrid odor appears. The constant accumulation of lubricant leads to chronic balanitis, or worse, malignant tumors develop.
The urethral glands secrete a colorless liquid called urethral rhea. It serves to protect the urethra. Its appearance is associated with strong arousal during erection. The volume of secretions depends on the physiological characteristics of each organism, but after a long period of refusal from sex, the amount increases.
In the morning, wet dreams (spontaneous discharge of semen) that are not associated with sex are possible. Pollution is possible in both adolescents and mature men who have not had sexual intercourse for a long time.
With strong tension of the abdominal muscles, a small amount of translucent mucus is released from the urethra. Also, prostatorrhea can occur during constipation.
Pathological changes in discharge
Abnormal discharge from the penis may indicate a sexually transmitted disease (STD), cancer, nonspecific inflammation, or genital trauma.
It is possible to distinguish from ordinary secretions those that are associated with a pathological nature, possibly by their nature, smell, color:
- the volume of discharge has become much more abundant or, conversely, decreased;
- the color has changed, the discharge has become cloudy;
- there were impurities of blood, pus, lumps of mucus;
- change in structure: the discharge became sticky and thick;
- the smell has become fishy, sour, or putrid;
- unpleasant sensations appear when urinating.
If you notice any change in your discharge, it is dangerous to self-medicate. It is necessary to seek medical advice as soon as possible, be sure to undergo tests, and also take a smear.
Discharge characteristic of STDs
Discharges that become very viscous and have a transparent color, as a rule, are a chronic form of mycoplasmosis and ureaplasmosis, chlamydia. When analyzing, leukocytes are found in the field of view up to 5 units.
If the discharge has become white and translucent, then this indicates the presence of an acute form of mycoplasmosis, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis.
Discharge with purulent blotches and a characteristic odor is a sign of gonorrhea. Their structure is very thick and sticky, the color is greenish-yellow. In laboratory tests, a large number of leukocytes are detected. Painful sensations when urinating are also noted.
Infections with multiple pathogens are common in STDs. The symptoms and nature of the discharge take on a completely different look, so it is very important to conduct high-quality laboratory tests to identify the true causative agents of the disease.
Non-venereal inflammation and discharge in men
Non-venereal inflammation occurs when nonspecific bacteria enter the pelvic organs, and can also be the result of immune problems. Own microflora becomes conditionally pathogenic, when pathogenic bacteria, which are in small numbers, begin to prevail over beneficial bacteria, thereby causing non-venereal inflammation.
Non-gonorrheal urethritis is characterized by discharge in the form of purulent lumps in small quantities. There is a frequent urge to urinate, an itching sensation. Infection is ascending, first infecting the bladder, then the kidneys. When the kidneys become infected, the discharge contains blood. This is a very dangerous symptom.
Fungi of the genus Candida cause candidiasis. An increase in the number of these fungi occurs with a weakening of their own immunity, as well as after taking antibiotics. Symptoms include discharge that resembles cottage cheese in structure. There is a sour odor, itching sensations, especially when urinating.
Gardnerellosis of the urethra is determined by a specific fishy odor, the discharge becomes yellow-green in color, of a small volume. This infection occurs when there is a violation in the microflora, in other words, when dysbiosis appears.
If the foreskin becomes inflamed (balanoposthitis), the discharge becomes purulent and mucus. The head of the penis turns red and becomes very painful.
Prostatitis manifests itself as a cloudy discharge that appears at the end of urination. This disease has serious complications such as lack of erection and complete impotence, anuria.
Discharge uncharacteristic of inflammation
Spermatorrhea is passive leakage of semen, without masturbation or intercourse. This disease is most often the result of stress, neurosis or diseases of the spine. With spermatorrhea, the ducts are innervated.
Bloody discharge can appear after trauma to the urethral canal, taking a smear, inserting a catheter, as well as when sand or small stones pass through the urethral canal. In this case, the hematorrhea is very painful.
A serious symptom is brown discharge with pus and blood - they indicate the presence of a malignant tumor.
If you find any uncharacteristic discharge in yourself, you should immediately contact a medical institution and take the necessary tests. The sooner the correct diagnosis is made, the sooner recovery will come.
How is the examination going?
- First of all, an examination of the penis is carried out. The procedure is necessary to identify traces of trauma to the head and foreskin. Look out for a rash or discharge.
- Obligatory examination and palpation of the lymph nodes in the groin, determination of their size, condition, temperature.
- Sampling of secretions from the prostate for laboratory research - for this, prostate massage is done through the rectum.
In the laboratory, under a microscope, a study of the collected material is carried out:
- a smear can determine the maturity of leukocytes, their number in the field of view. An increased amount indicates acute urethritis or a chronic inflammatory process;
- an increased number of eosinophils indicates an allergic process in the urethra;
- when erythrocytes are detected, we can talk about tumors, serious inflammation;
- if the amount of epithelium exceeds the norm, then we are talking about chronic urethritis;
- the smear contains sperm - spermatorrhea;
- mucus is found in the smear - urethrorrhea;
- lipid grains are present in the smear - prostatorrhea.
For reliable results, you must follow some rules: do not wash yourself before taking the material, do not have sex a day before the analysis, do not go to the toilet for a few hours before taking a smear.
LHC-inoculation is needed to identify the largest number of microorganisms belonging to the same species. Their properties are being studied for further diagnosis of the infection. A general analysis of blood and urine is taken. An ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs and the prostate is carried out, if necessary, according to indications, then tomography.
Any uncharacteristic discharge is a serious reason to see a doctor. You cannot self-medicate, even if the illness seems obvious to you. In this way, complications can be earned that are difficult to treat even with the strongest antibiotics. The inflammatory process will not stop, but will only acquire a latent form, which is fraught with serious complications, up to and including death.
Preventive measures
Any disease is easier to prevent than to cure, therefore, observing simple rules of personal hygiene, you can protect yourself from many problems. In addition, there are a few more rules:
- underwear should be made of natural materials, not tight;
- proper contraception is needed;
- casual sex should be avoided.
Compulsory treatment of both partners is necessary if a venereal disease is detected in at least one of them. Otherwise, re-infection will constantly occur, which is dangerous with a transition to a chronic form and even infertility.